SNAKE
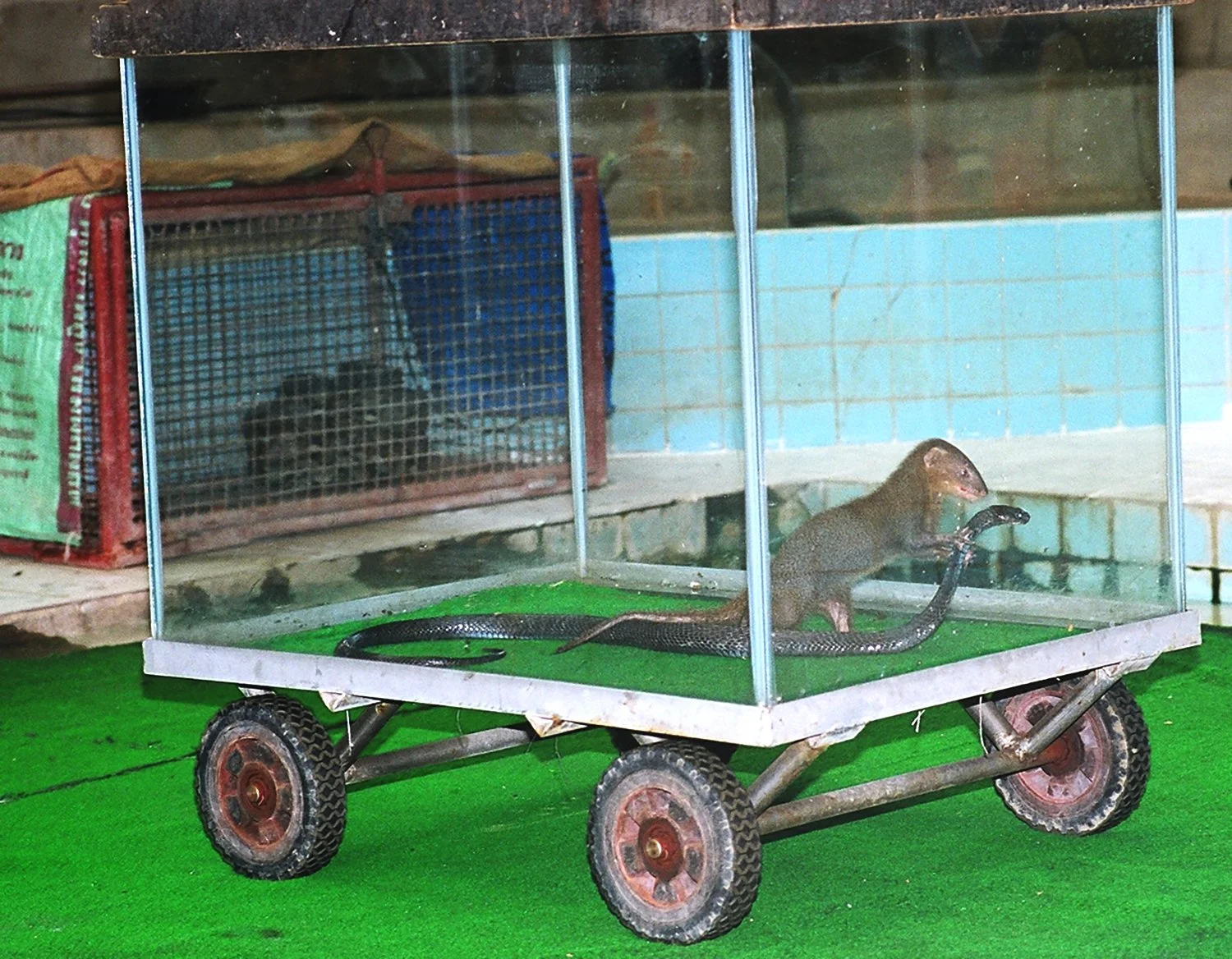
Why is the mongoose immune to the poison of the snake?
The reason is that mongooses make a glycoprotein that binds to the protein in the venom so a moderate amount of snake venom won't hurt them.
Reptiles were on the earth 275 million years ago and it is believed that a type of ancient reptile known as the Cotylosours is the ancestor of all reptiles. Several million years later many branches of reptiles split off from the original Cotylosours and one branch developed into the present day turtle, another branch became the mammals, and another became dianasours, which remain as crocodiles, birds and a family of lizards.
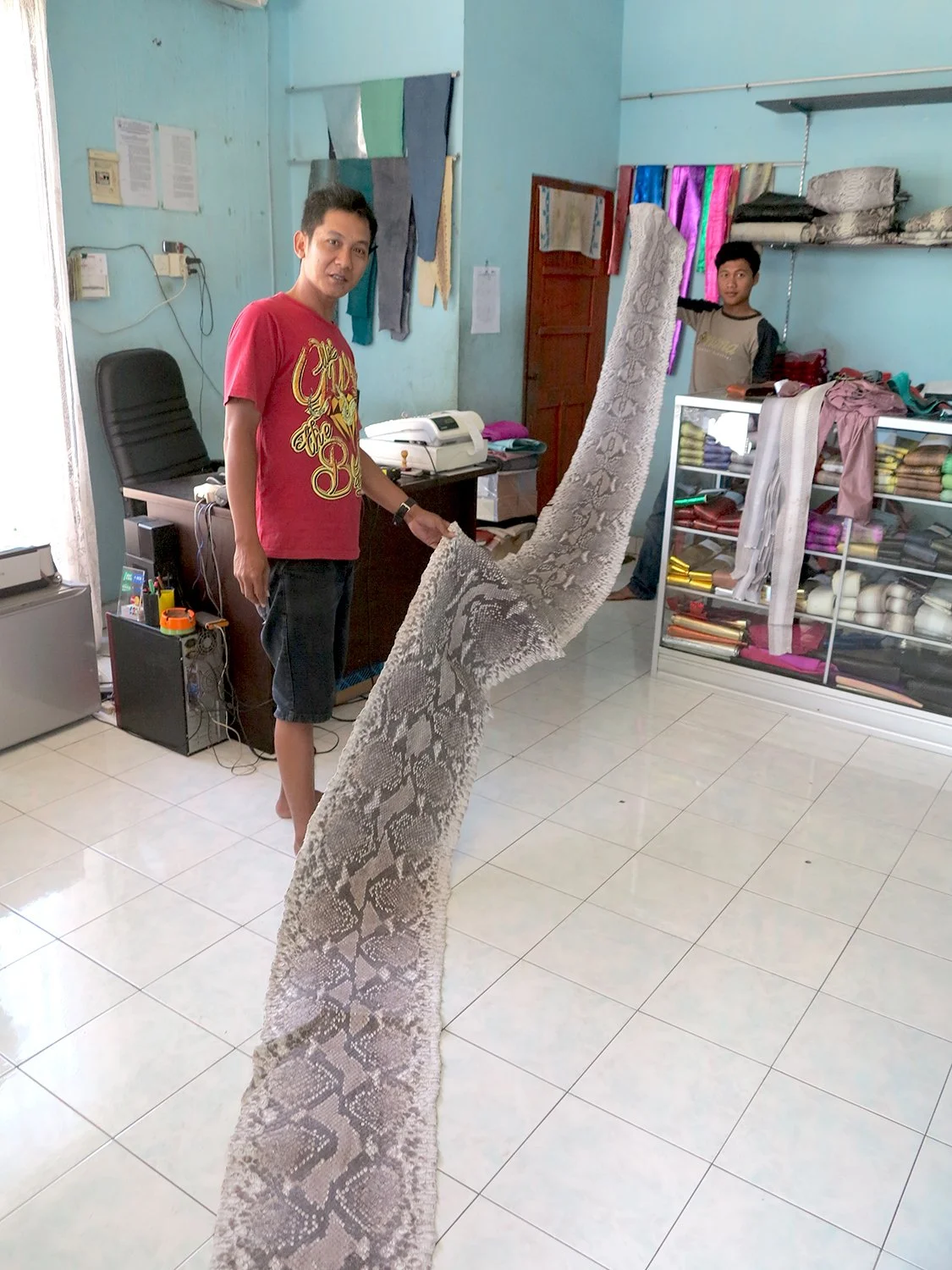
King Cobra, though not actually a cobra at all, is the longest venomus snake at about 18.5 ft. The venom from this snake can easily kill a human and is one of the most dangerous snakes in Asia.
Its venom injects 380-600 mg of venom which is enough to kill 20-40 people in a single bite and can kill an elephant in 3 hours. Death in 15 minutes for a human.
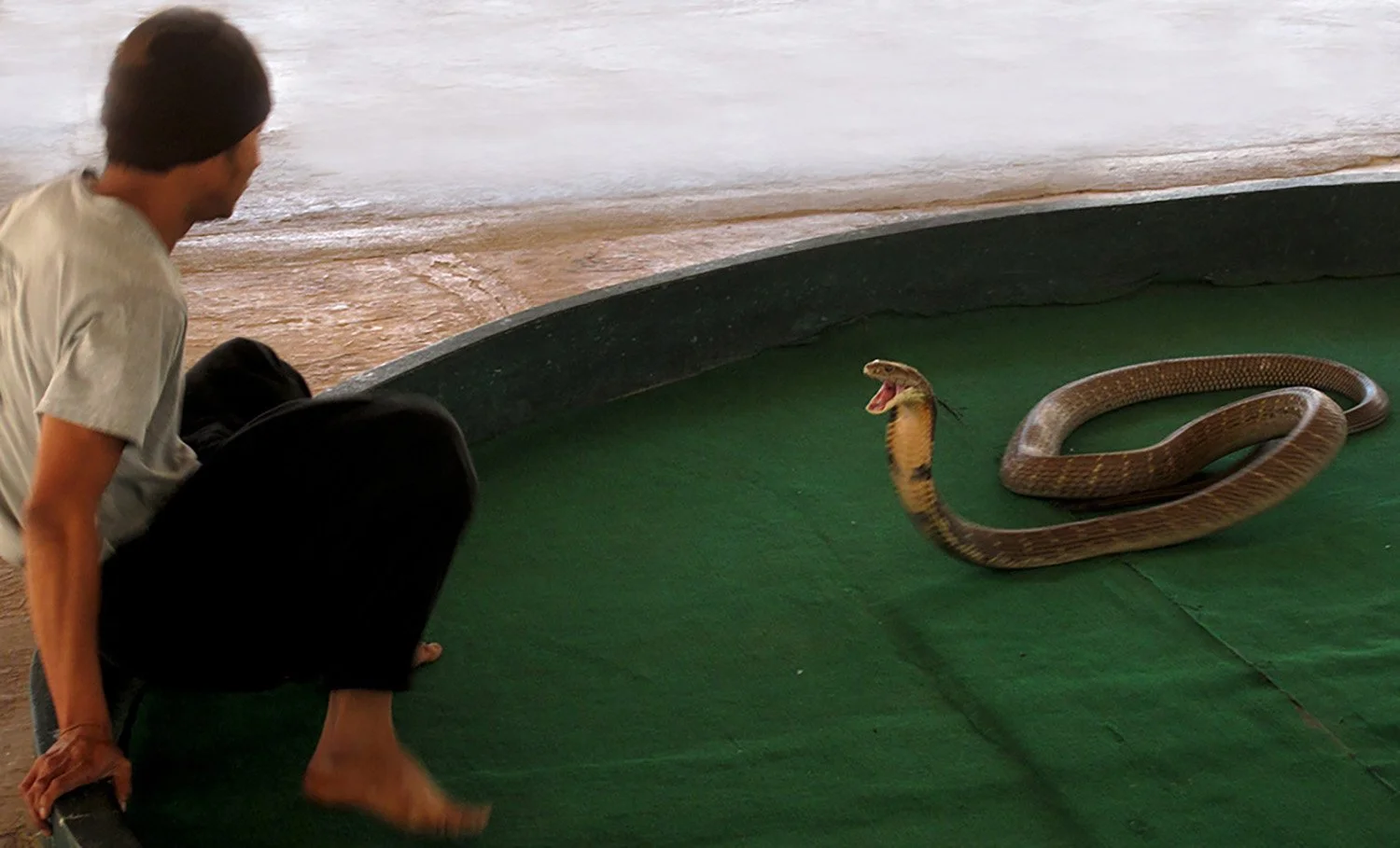
Cobra receptors have a unique sugar molecule that acts as an umbrella, blocking the toxin from binding to the receptor, hence they are immune to their own venom. If the that sugar molecule is removed the cobra becomes toxin-sensitive. The only animal in the world with that same sugar molecule sitting on that same receptor is the mongoose, which also happens to be the one of the very few animals a cobra can’t kill.
The company Mannatech has promoted its Advanced Ambrotose health supplement as assisting with cell to cell communication and the king cobra and mongoose examplify the truth in the power of sugar molecules.